The iDI-NAV tool ©
What is it?
The Interactive Diversity and Inclusion Navigator® (iDI-Nav®) is an innovative, research-based, online tool designated to identify and measure the diversity and inclusion (D&I) barriers experienced by employees in the workplace.
The iDI-Nav® aims to support companies to create, benchmark and/or improve their D&I policies and inclusion culture.
The tool is unique in the D&I field offering a comprehensive, in-depth, data-based ranked mapping of the 30 most referenced D&I barriers as experienced by employees. It is supported by a proprietary algorithm that measures and weights the D&I barriers so to assess their ranking importance for the workforce. Its added value lies in the comprehensiveness, bottom-up real, time approach, and customization.
How does it work?
The iDI-Nav® tool applies a systematic approach on D&I data collection and analysis consisting of four steps.
In the first step, the employees fill in the iDI-Nav® survey, which is developed using an innovative survey method (Best-Worst-Scaling combined with Hierarchical Bayes data analysis). Each participant fills in a fully anonymized questionnaire.
In the second step, the iDI-Nav® tool processes the collected data. The analysis leads to so-called relative importance scores, indicating each barrier’s importance, relative to other barriers. The relative importance scores are illustrated graphically in a customized iDI-Nav® map:
The length of each of the rays illustrates the barrier’s relative importance score. The higher the length, the more important the barrier is for the employees in the examined workplace. The relative importance scores of all barriers adds up to 100.
In the third step, the D&I barriers are grouped into five sub-categories: Individual, Domestic, Social, Organizational, and Cultural. This step encompasses the iDI-Nav® algorithm which generates a score for each of the five subcategories, in the scale of 0 (no barriers experienced by the employees) to 100 (maximum manifestation of all barriers). The higher the score, the more hindering the employees perceive the barriers within each sub-category.
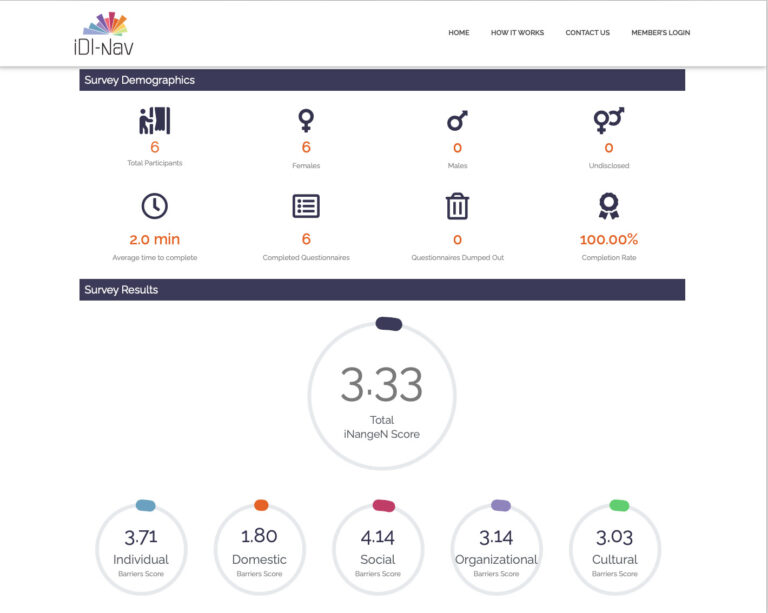
In the fourth step, an iDI-Nav® report is prepared analyzing the findings of the iDI-Nav® tool as per the participants demographics and contributions as well as against the organization’s D&I policies. The iDI-Nav® report takes a deep dive into the real D&I experiences and needs of the employees and compares the findings against the applied D&I policies. Then, evidence-based recommendations are proposed for optimization of D&I policies in alignment with the organization’s goals and priorities.
The iDI-Nav® tool is available in multiple languages
iDI-Nav® is currently available in four languages (English, German, French, Greek); translation into more languages will be added
The 30 D&I barriers of iDI-Nav®
The following description of the D&I barriers has been drawn from published literature, is indicative and aims to provide clarification within the framework of the iDI-Nav® tool application.
A comprehensive description of the D&I barriers involves multi-disciplinary and multi-dimensional approach which does not fall within the scope of this tool.
- Age | Age as a career barrier. Older employees experience age-based multiple discrimination reducing structurally their choices for work or working arrangements.
- Lack of equal career advancement opportunities | Unequal access to career advancement opportunities affected by rigid criteria for promotion and recognition and luck of suitable policies to support them.
- Culture | Cultural and organizational barriers that generate (in)direct discrimination against career advancement and pursue of decision making positions.
- Lack of family (espousal) support | Absence of sources of support including partners and other family members.
- Gender bias (discrimination) | Prejudiced actions or thoughts based on the gender-based perceptions on inequality between genders in rights and dignity. (In)direct discrimination, such as any distinction, exclusion or restriction made on the basis of gender and/or sex which has the effect or purpose of impairing or nullifying the recognition, enjoyment or exercise of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural, civil or any other field.
- Gender gap | Gap in any area between genders in terms of their levels of participation, access, rights, remuneration or benefits.
- Gender pay gap | Unequal pay for equal work or work of equal value. Unequal pay for work to which equal value is attributed, without any (in)direct discrimination with regard to all aspects of pay and conditions of remuneration.
- Glass ceiling | artificial impediments and invisible barriers that militate against women’s access to top decision-making and managerial positions in an organization, whether public or private and in whatever domain. Also knows as “sticky floor”.
- Glass cliff | Phenomenon whereby individuals belonging to particular groups are more likely to be found in leadership positions that are associated with a greater risk of failure and criticism.
- Isolation | Predominance of “old boys clubs”, inflexible corporate cultures and male dominated leadership teams that do not support or enable women and/or members from the LGBTI community to move into comparable leadership roles.
- Lack of executive sponsor | Inactive and/or ineffective senior leader to support the successful career advancement to leadership roles (also known “executive buy-in for senior development positions”).
- Lack of flexible working environment | Lack of flexibility of working time arrangements such as working time, part-time work, overtime and night work in a flexible way.
- Lack of confidence | Self-doubt, under-estimating personal capabilities.
- Lack of mentoring | Limited access to capable mentors and effective mentoring (sheltered relationship that allows learning and experimentation to take place and personal potential and new skills to flourish through a process in which one person, the mentor, supports the career and development of another, the mentee, outside the normal superior–subordinate relationship).
- Lack of networking | Lack of informal networks development (informal networks can shape career trajectories by regulating access to jobs, channeling the flow of information and referrals, creating influence and reputation, supplying emotional support, feedback, political advice and protection).
- Lack of leadership skills | Lack of leadership skills to address the particular challenges when transitioning to more senior leadership roles.
- Personal health | Devalue and marginalize employees and issues associated with gender and sex related health.
- Queen bee syndrome | The reluctance of successful women to support other women.
- Race discrimination | Discrimination where one person is treated less favorably on the grounds of its racial origin than another person is, has been or would be treated in a comparable situation.
- Lack of role model | The lack of a person looked to by others as an example to be imitated or whose behavior, example, or success is or can be emulated by others in any domain (eg. business, education, science, art, etc).
- Sexual harassment | Unwanted conduct related to the sex of a person occurring with the purpose or effect of violating the dignity of that person, and of creating an intimidating, hostile, degrading, humiliating or offensive environment. An unwelcome behavior of sexual nature that if allowed to continue could create a hostile work environment for the recipient.
- Lack of social support | Resistance of societal culture to gender equality, diversity and inclusion; non-adoption of new norms, beliefs and cultures.
- Stereotypes | Preconceived ideas whereby men and women are arbitrarily assigned characteristics and roles determined and limited by their gender creating a heavily gendered work environment. Gender stereotype that limits women’s gaining of personal abilities, pursuing their professional careers and making choices about their lives and life plans.
- Limited succession planning | Limited participation in succession planning process by which individuals are scanned to pass on the leadership role within an organization.
- Tokenism | Policy or practice that is mainly symbolic, and involves attempting to fulfil one’s obligations with regard to established targets, such as voluntary or mandated gender quotas, with limited efforts or gestures, especially towards minority groups and women, in ways that will not change men-dominated power and/or organizational arrangements.
- Work/life balance | Achieving balance between not only domestic tasks and caring for dependent relatives, but also extracurricular responsibilities or other important life priorities. The need to successfully reconcile professional and family obligations.
- Ethnicity | Discrimination where one person is treated less favorably on the grounds of its ethnicity than another person is, has been or would be treated in a comparable situation.
- Religion | Discrimination where one person is treated less favorably on grounds of its religion or belief than another person is, has been or would be treated in a comparable situation.
- Sexual orientation | Discrimination where one person is treated less favorably on grounds of its sexual orientation or gender identity, than another person is, has been or would be treated in a comparable situation.
- Disability | Discrimination where one person is treated less favorably on the grounds of its disability than another person is, has been or would be treated in a comparable situation.
The results on the D&I barriers may be interpreted by studying the iDI-Nav® map which reflects both the actual range and the varying degree of D&I barriers’ prevalence within the explored organizational work setting. The “spikes” of the iDI-Nav® map depict the influence / prevalence of each barrier in a scale of 100 (min prevalence: 0; maximum prevalence: total average of best D&I level: 0; total average of worst D&I level:100) .
Realistically speaking, it is very difficult to achieve a perfect score, which would be the zero (0). In that case, no D&I barriers would exist. However, it may be argued that a D&I “healthy” organization is the organization that improves the D&I level in a steady and sustainable way.
This is to be decided by the organization. However, to get reliable and accurate results an adequately representative sample of the workforce is necessary. Therefore, the more participants, the better.
For start, no data are exchanged with client’s computer systems. This ensures that nobody in the organization can relate an employee with his questionnaire answers. Secondly, we have implemented full encryption in the whole operation cycle of the survey process. This means that there is no personal data or tokens are transmitted or stored in human readable form. And because no computer system is 100% secure, you can be sure that in case of a successful attack, the data will be useless to the attacker.
The time needed to fill in the survey ranges between 8 and 15 minutes.
The pricing strategy is cost-efficient and depends on several variables such as the number of participants, the number of applications of the iDI-Nav® tool, etc. Please contact us [HERE] for more information.

